Qt Quick 3D Physics - キャノンの例
物理オブジェクトをスポーンする方法を示します。
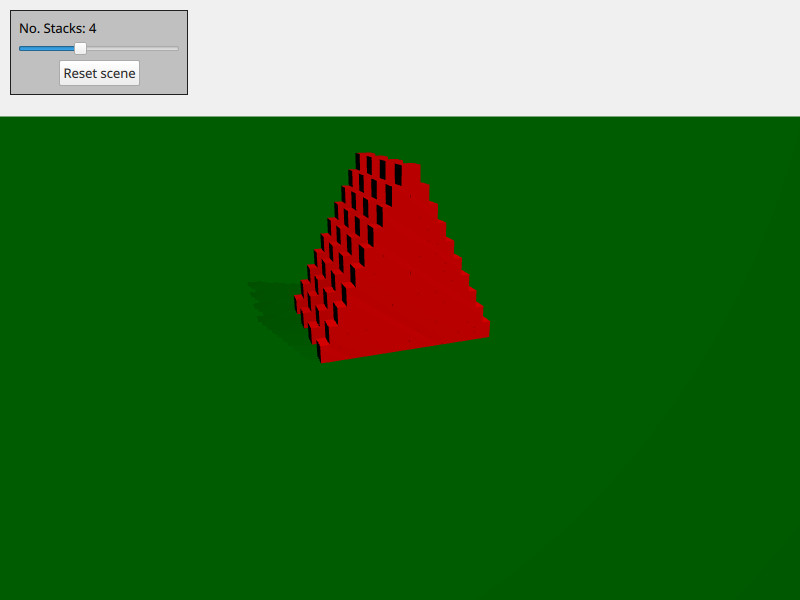
この例では、物理オブジェクトをオンデマンドで作成および削除する方法を示します。シーンは、いくつもの箱の積み重ねで構成されています。WASD とマウスを使って移動し、space を押してボールを撃つことができます。
シーンには、ビュー、カメラ、ライトなど、Qt Quick 3Dオブジェクトがセットアップされています:
PerspectiveCamera { id: camera position: Qt.vector3d(-4000, 5000, 10000) eulerRotation: Qt.vector3d(-20, -20, 0) clipFar: 200000 clipNear: 100 } DirectionalLight { eulerRotation: Qt.vector3d(-45, 45, 0) castsShadow: true brightness: 1 shadowMapQuality: Light.ShadowMapQualityVeryHigh shadowMapFar: camera.clipFar shadowFactor: 50 csmNumSplits: 2 csmSplit1: 0.1 csmSplit2: 0.3 softShadowQuality: Light.PCF4 }
静的な床も追加します:
StaticRigidBody { eulerRotation: Qt.vector3d(-90, 0, 0) collisionShapes: PlaneShape {} Model { source: "#Rectangle" scale: Qt.vector3d(2000, 2000, 1) materials: PrincipledMaterial { baseColor: "green" } castsShadows: false receivesShadows: true } }
オブジェクトのスポナーとして使うノードを作り、ビューの中に入れます:
Node { id: shapeSpawner property var instancesBoxes: [] property var instancesSpheres: [] property int stackCount: 0 property var boxComponent: Qt.createComponent("Box.qml") property var sphereComponent: Qt.createComponent("Sphere.qml") function createStack(stackZ, numStacks) { let size = 10 let extents = 400 for (var i = 0; i < size; i++) { for (var j = 0; j < size - i; j++) { let x = j * 2 - size + i let y = i * 2 + 1 let z = 5 * (stackZ - numStacks) let center = Qt.vector3d(x, y, z).times(0.5 * extents) let box = boxComponent.incubateObject(shapeSpawner, { "position": center, "xyzExtents": extents }) instancesBoxes.push(box) } } } function createBall(position, forward) { var diameter = 600 var speed = 20000 let settings = { "position": position, "sphereDiameter": diameter } let sphere = sphereComponent.createObject(shapeSpawner, settings) sphere.setLinearVelocity(forward.times(speed)) instancesSpheres.push(sphere) if (sphere === null) { console.log("Error creating object") } } function reset() { // Only run method if previous stack has been created fully for (var i = 0; i < instancesBoxes.length; i++) if (!instancesBoxes[i].object) return instancesSpheres.forEach(sphere => { sphere.collisionShapes = [] sphere.destroy() }) instancesBoxes.forEach(box => { box.object.collisionShapes = [] box.object.destroy() }) instancesSpheres = [] instancesBoxes = [] for (var stackI = 0; stackI < stackSlider.value; stackI++) { shapeSpawner.createStack(stackI, stackSlider.value) } } }
スタックを作るためのcreateStack 、速度のあるボールを作るためのcreateBall 、シーンをリセットするためのreset 。実際にスポーンされる箱と球は、それぞれのqmlファイル(box.qml とsphere.qml )に格納されています。
ファイル
© 2025 The Qt Company Ltd. Documentation contributions included herein are the copyrights of their respective owners. The documentation provided herein is licensed under the terms of the GNU Free Documentation License version 1.3 as published by the Free Software Foundation. Qt and respective logos are trademarks of The Qt Company Ltd. in Finland and/or other countries worldwide. All other trademarks are property of their respective owners.

