Qt Quick 3D Physics - 質量の例
物体の質量と慣性を設定するさまざまな方法を示します。
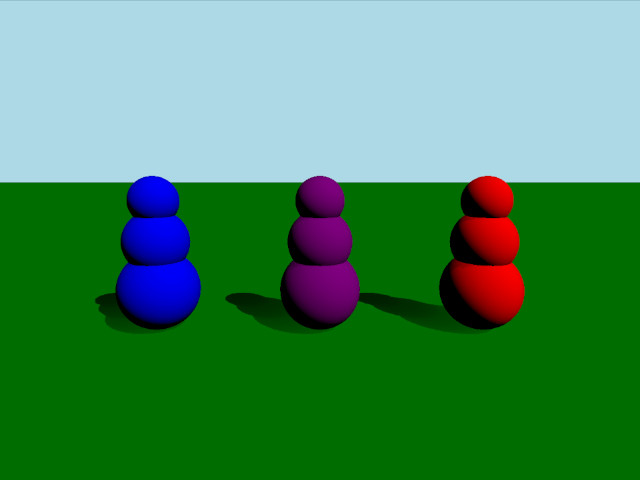
この例題は、ボディの質量と慣性を設定する3つの異なる方法を示します。シーンは、垂直に積み重ねられた3つの球体からなる3つのボディで構成されています。これらの物体はすべて同じ質量を持っていますが、質量中心と慣性テンソルが異なるため、衝突したときの挙動が異なります。
セットアップ
まず、PhysicsWorld を追加します:
PhysicsWorld { running: true gravity: Qt.vector3d(0, -9.81, 0) typicalLength: 1 typicalSpeed: 10 scene: viewport.scene }
環境、カメラ、ライトをセットアップします:
environment: SceneEnvironment { clearColor: "lightblue" backgroundMode: SceneEnvironment.Color } PerspectiveCamera { id: camera position: Qt.vector3d(0, 2, 5) eulerRotation: Qt.vector3d(-10, 0, 0) clipFar: 100 clipNear: 0.01 } DirectionalLight { eulerRotation.x: -45 eulerRotation.y: 45 castsShadow: true brightness: 1 shadowFactor: 50 shadowBias: 0.1 pcfFactor: 0.01 }
物理オブジェクト
通常の静的平面を用意します:
StaticRigidBody { position: Qt.vector3d(0, 0, 0) eulerRotation: Qt.vector3d(-90, 0, 0) collisionShapes: PlaneShape {} Model { source: "#Rectangle" materials: PrincipledMaterial { baseColor: "green" } castsShadows: false receivesShadows: true } }
RolyPolyと呼ぶことにします。RolyPolyは、いわゆるローリーポリのおもちゃのように振る舞うからです。RolyPolyはDynamicRigidBody 、3つの球形のコリジョンシェイプを持っています:
DynamicRigidBody { property string color: "blue" collisionShapes: [ SphereShape { id: sphere0 diameter: 1 }, SphereShape { id: sphere1 diameter: 0.8 position: Qt.vector3d(0, 0.6, 0) }, SphereShape { id: sphere2 diameter: 0.6 position: Qt.vector3d(0, 1.1, 0) } ] Model { source: "#Sphere" position: sphere0.position scale: Qt.vector3d(1,1,1).times(sphere0.diameter*0.01) materials: PrincipledMaterial { baseColor: color } } Model { source: "#Sphere" position: sphere1.position scale: Qt.vector3d(1,1,1).times(sphere1.diameter*0.01) materials: PrincipledMaterial { baseColor: color } } Model { source: "#Sphere" position: sphere2.position scale: Qt.vector3d(1,1,1).times(sphere2.diameter*0.01) materials: PrincipledMaterial { baseColor: color } } }
次に、3つのRolyPolyをシーンに追加します:
RolyPoly { position: Qt.vector3d(-2, 0.5, 0) color: "blue" mass: 0.9 centerOfMassPosition: Qt.vector3d(0, -0.5, 0) inertiaTensor: Qt.vector3d(0.217011, 0.0735887, 0.217011) massMode: DynamicRigidBody.MassAndInertiaTensor } RolyPoly { position: Qt.vector3d(0, 0.5, 0) color: "purple" mass: 0.9 centerOfMassPosition: Qt.vector3d(0, -0.5, 0) inertiaTensor: Qt.vector3d(0.05, 100, 100) massMode: DynamicRigidBody.MassAndInertiaTensor } RolyPoly { position: Qt.vector3d(2, 0.5, 0) color: "red" mass: 0.9 massMode: DynamicRigidBody.Mass }
紫と青のローリーポリーには、カスタムの質量中心と慣性テンソルがあります。ボディはデフォルトで均一な密度を使用し、自動的に質量と慣性を計算するので、紫と青のボディではmassModeをDynamicRigidBody.MassAndInertiaTensorに設定し、代わりに提供された質量と慣性テンソルを使用します。質量中心を低くすることで、押し倒された後でも常にボディが立つようになる。紫色のボディの慣性テンソルは、一方向にはふらつきやすいが、もう一方にはほとんどふらつかないようにする。赤いボディは自動的に計算された重心を持つので、倒されても横たわり続ける。
ボールを撃つ
異なるボディの挙動をテストするために、ボールを撃つためのノードを追加します:
Node { id: shapeSpawner property var spheres: [] property var sphereComponent: Qt.createComponent("Sphere.qml") function createBall(position, forward) { let diameter = 0.2 let speed = 20 let sphere = sphereComponent.createObject(shapeSpawner, { "position": position, "sphereDiameter": diameter }) sphere.setLinearVelocity(forward.times(speed)) var pair = { "sphere": sphere, "date": Date.now() } spheres.push(pair) if (sphere === null) { console.log("Error creating object") } } function clean() { spheres = spheres.filter(sphere => { let diff = Date.now() - sphere['date']; if (diff > 5000) { sphere['sphere'].destroy(); return false; } return true; }); } Timer { interval: 200 running: true repeat: true onTriggered: shapeSpawner.clean() } }
次に、WasdController を追加して、カメラを動かし、ボディにボールを向けて撃つことができるようにします:
WasdController { speed: 0.01 shiftSpeed: 0.1 controlledObject: camera Keys.onPressed: (event) => { handleKeyPress(event); if (event.key === Qt.Key_Space) { shapeSpawner.createBall(camera.position, camera.forward); } } Keys.onReleased: (event) => { handleKeyRelease(event) } }
ファイル
© 2025 The Qt Company Ltd. Documentation contributions included herein are the copyrights of their respective owners. The documentation provided herein is licensed under the terms of the GNU Free Documentation License version 1.3 as published by the Free Software Foundation. Qt and respective logos are trademarks of The Qt Company Ltd. in Finland and/or other countries worldwide. All other trademarks are property of their respective owners.

