Qt Quick 3D Physics - 複合形状の例
複雑なコリジョンシェイプの使い方を説明します。
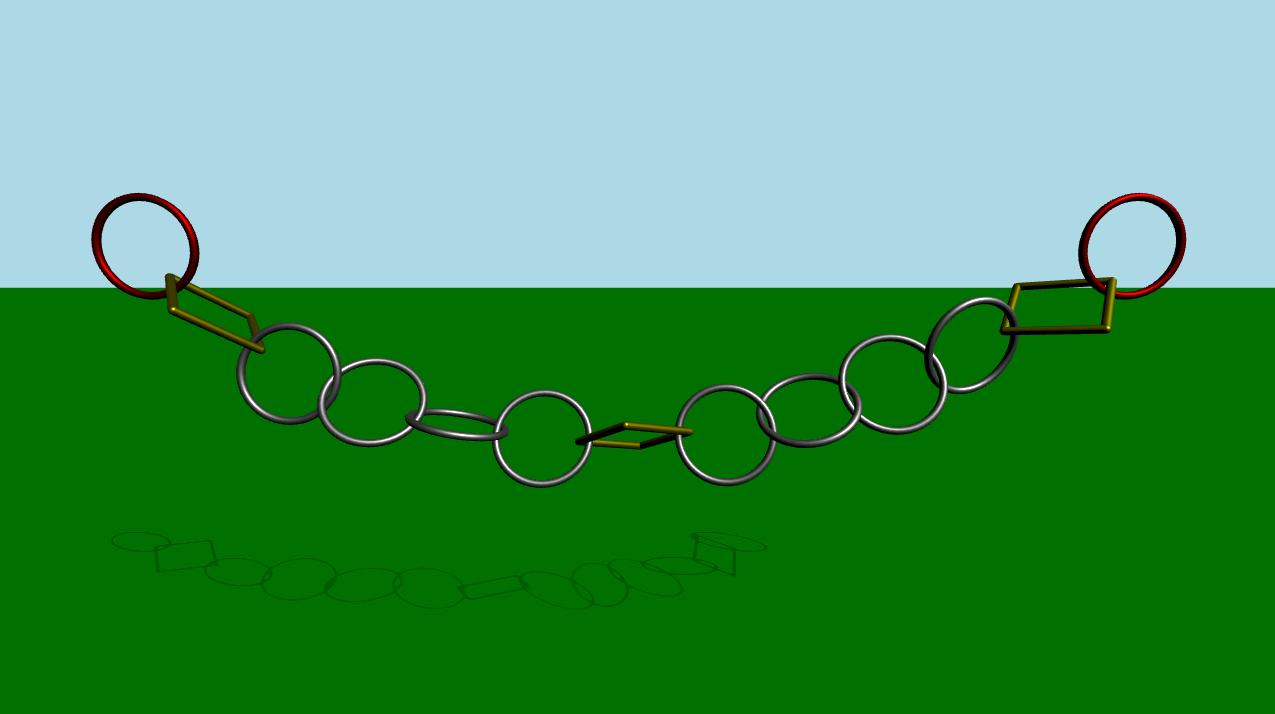
この例では、複数のコリジョンシェイプを使用して、衝突検出用の複雑なオブジェクトを作成する方法を示します。シーンは、緑色の静的な平面と、互いに接続された一連のリンクで構成されています。最初、シミュレーションは無効になっています。しばらくして、あるいはユーザーがスペースキーを押すと、シミュレーションが始まります。左端と右端のリンクが水平に前後に動くアニメーションが始まります。
セットアップ
いつものように、PhysicsWorld :
PhysicsWorld { id: physicsWorld enableCCD: true maximumTimestep: 20 scene: viewport.scene }
環境、カメラ、ライトを用意する:
environment: SceneEnvironment { antialiasingMode: SceneEnvironment.MSAA backgroundMode: SceneEnvironment.Color clearColor: "lightblue" } focus: true PerspectiveCamera { id: camera position: Qt.vector3d(0, 900, 1500) eulerRotation: Qt.vector3d(-10, 0, 0) clipFar: 15500 clipNear: 1 } DirectionalLight { eulerRotation.x: -45 eulerRotation.y: 45 castsShadow: true brightness: 1.5 shadowMapQuality: Light.ShadowMapQualityHigh }
物理オブジェクト
通常の静的な平面を用意します:
StaticRigidBody { position: Qt.vector3d(0, -100, 0) eulerRotation: Qt.vector3d(-90, 0, 0) collisionShapes: PlaneShape {} Model { source: "#Rectangle" scale: Qt.vector3d(500, 500, 1) materials: PrincipledMaterial { baseColor: "green" } castsShadows: false receivesShadows: true } }
次に、リンクのインスタンスを作ります。
MeshLink { id: leftLink isKinematic: true property vector3d startPos: Qt.vector3d(-6 * viewport.ringDistance, viewport.ringY, 0) property vector3d startRot: Qt.vector3d(90, 0, 0) kinematicPosition: startPos position: startPos kinematicEulerRotation: startRot eulerRotation: startRot color: "red" } CapsuleLink { position: Qt.vector3d(-5 * viewport.ringDistance, viewport.ringY, 0) eulerRotation: Qt.vector3d(90, 0, 0) } MeshLink { position: Qt.vector3d(-4 * viewport.ringDistance, viewport.ringY, 0) eulerRotation: Qt.vector3d(90, 0, 0) } MeshLink { position: Qt.vector3d(-3 * viewport.ringDistance, viewport.ringY, 0) eulerRotation: Qt.vector3d(0, 90, 0) } MeshLink { position: Qt.vector3d(-2 * viewport.ringDistance, viewport.ringY, 0) eulerRotation: Qt.vector3d(90, 0, 0) } MeshLink { position: Qt.vector3d(-1 * viewport.ringDistance, viewport.ringY, 0) eulerRotation: Qt.vector3d(0, 90, 0) } CapsuleLink { position: Qt.vector3d(0, viewport.ringY, 0) } MeshLink { position: Qt.vector3d(1 * viewport.ringDistance, viewport.ringY, 0) eulerRotation: Qt.vector3d(0, 90, 0) } MeshLink { position: Qt.vector3d(2 * viewport.ringDistance, viewport.ringY, 0) eulerRotation: Qt.vector3d(90, 0, 0) } MeshLink { position: Qt.vector3d(3 * viewport.ringDistance, viewport.ringY, 0) eulerRotation: Qt.vector3d(0, 90, 0) } MeshLink { position: Qt.vector3d(4 * viewport.ringDistance, viewport.ringY, 0) eulerRotation: Qt.vector3d(90, 0, 0) } CapsuleLink { position: Qt.vector3d(5 * viewport.ringDistance, viewport.ringY, 0) eulerRotation: Qt.vector3d(90, 0, 0) } MeshLink { id: rightLink isKinematic: true property vector3d startPos: Qt.vector3d(6 * viewport.ringDistance, viewport.ringY, 0) property vector3d startRot: Qt.vector3d(90, 0, 0) kinematicPosition: startPos position: startPos kinematicEulerRotation: startRot eulerRotation: startRot color: "red" }
左側の最初のリンクは、アニメーションでコントロールできるように、isKinematic プロパティをtrue に設定します。これはキネマティックオブジェクトなので、kinematicPosition とkinematicRotation プロパティを設定する必要があります。アニメーションは、kinematicPosition プロパティをアニメーションさせることで行います。他のリンクは、いくつかの間隔を空けてインスタンス化されています。
物理的なシミュレーションに正確に追従する滑らかなアニメーションを得るために、AnimationController を使い、PhysicsWorld のonFrameDone 信号に接続します。こうすることで、シミュレーションが遅くなるようなコマ落ちがあっても、アニメーションはそれに応じて遅くなります。左端と右端のリングを前後に動かすために、4つのNumberAnimation を持つSequentialAnimation を使います。これがアニメーションのQMLコードです:
Connections { target: physicsWorld property real totalAnimationTime: 12000 function onFrameDone(timeStep) { let progressStep = timeStep / totalAnimationTime animationController.progress += progressStep if (animationController.progress >= 1) { animationController.completeToEnd() animationController.reload() animationController.progress = 0 } } } AnimationController { id: animationController animation: SequentialAnimation { NumberAnimation { target: leftLink property: "kinematicPosition.x" to: 3 * viewport.ringDistance from: -6 * viewport.ringDistance easing.type: Easing.InOutCubic duration: 1000 } NumberAnimation { target: leftLink property: "kinematicPosition.x" from: 3 * viewport.ringDistance to: -6 * viewport.ringDistance easing.type: Easing.InOutCubic duration: 1000 } NumberAnimation { target: rightLink property: "kinematicPosition.x" to: -3 * viewport.ringDistance from: 6 * viewport.ringDistance easing.type: Easing.InOutCubic duration: 1000 } NumberAnimation { target: rightLink property: "kinematicPosition.x" from: -3 * viewport.ringDistance to: 6 * viewport.ringDistance easing.type: Easing.InOutCubic duration: 1000 } } }
興味深いのは、MeshファイルとCapsule Linksファイルの中で起こっていることです。それぞれのファイルを見てみよう。
メッシュリンク
DynamicRigidBody { scale: Qt.vector3d(100, 100, 100) property color color: "white" PrincipledMaterial { id: _material baseColor: color metalness: 1.0 roughness: 0.5 } Model { source: "meshes/ring.mesh" materials: [_material] } collisionShapes: [ ConvexMeshShape { source: "meshes/segmentedRing_001.mesh" }, ConvexMeshShape { source: "meshes/segmentedRing_002.mesh" }, ConvexMeshShape { source: "meshes/segmentedRing_003.mesh" }, ConvexMeshShape { source: "meshes/segmentedRing_004.mesh" }, ConvexMeshShape { source: "meshes/segmentedRing_005.mesh" }, ConvexMeshShape { source: "meshes/segmentedRing_006.mesh" }, ConvexMeshShape { source: "meshes/segmentedRing_007.mesh" }, ConvexMeshShape { source: "meshes/segmentedRing_008.mesh" }, ConvexMeshShape { source: "meshes/segmentedRing_009.mesh" }, ConvexMeshShape { source: "meshes/segmentedRing_010.mesh" }, ConvexMeshShape { source: "meshes/segmentedRing_011.mesh" }, ConvexMeshShape { source: "meshes/segmentedRing_012.mesh" } ] }
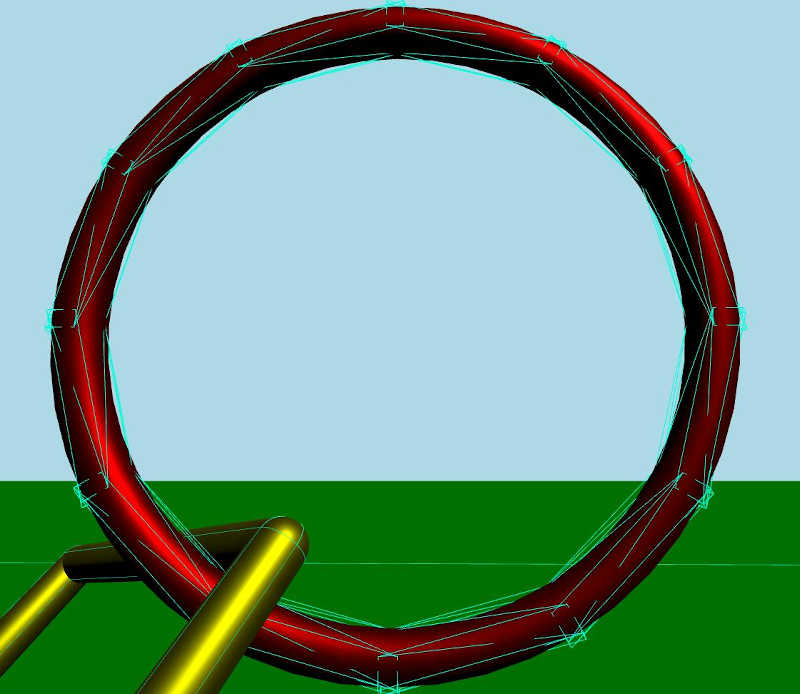
メッシュリンクは、モデルとマテリアルを持つダイナミック剛体です。モデルはメッシュファイルからメッシュをロードします。また、コリジョンシェイプのリストがあり、それらを組み合わせてコリジョン検出用の複合シェイプを形成します。各シェイプは、ソースファイルからメッシュをロードするコンベックスメッシュシェイプです。凸シェイプは基本的に、シェイプ内の任意の2点間の線が常にシェイプの内側にあるシェイプです。
デバッグモードが有効になっているときに詳しく見てみると、このようにコリジョンシェイプが複合コリジョンシェイプを形成している:
カプセルリンク
DynamicRigidBody { property real len: 170 property real w: 17 PrincipledMaterial { id: material3 baseColor: "yellow" metalness: 1.0 roughness: 0.5 } Node { opacity: 1 Model { materials: material3 source: "#Cylinder" scale: Qt.vector3d(w / 100, len / 100, w / 100) eulerRotation.z: 90 y: -len / 2 } Model { materials: material3 source: "#Cylinder" scale: Qt.vector3d(w / 100, len / 100, w / 100) eulerRotation.z: 90 y: len / 2 } Model { materials: material3 source: "#Cylinder" scale: Qt.vector3d(w / 100, len / 100, w / 100) x: len / 2 } Model { materials: material3 source: "#Cylinder" scale: Qt.vector3d(w / 100, len / 100, w / 100) x: -len / 2 } Model { materials: material3 source: "#Sphere" scale: Qt.vector3d(w / 100, w / 100, w / 100) x: -len / 2 y: -len / 2 } Model { materials: material3 source: "#Sphere" scale: Qt.vector3d(w / 100, w / 100, w / 100) x: -len / 2 y: len / 2 } Model { materials: material3 source: "#Sphere" scale: Qt.vector3d(w / 100, w / 100, w / 100) x: len / 2 y: -len / 2 } Model { materials: material3 source: "#Sphere" scale: Qt.vector3d(w / 100, w / 100, w / 100) x: len / 2 y: len / 2 } } collisionShapes: [ CapsuleShape { y: -len / 2 height: len diameter: w }, CapsuleShape { y: len / 2 height: len diameter: w }, CapsuleShape { x: -len / 2 eulerRotation.z: 90 height: len diameter: w }, CapsuleShape { x: len / 2 eulerRotation.z: 90 height: len diameter: w } ] }
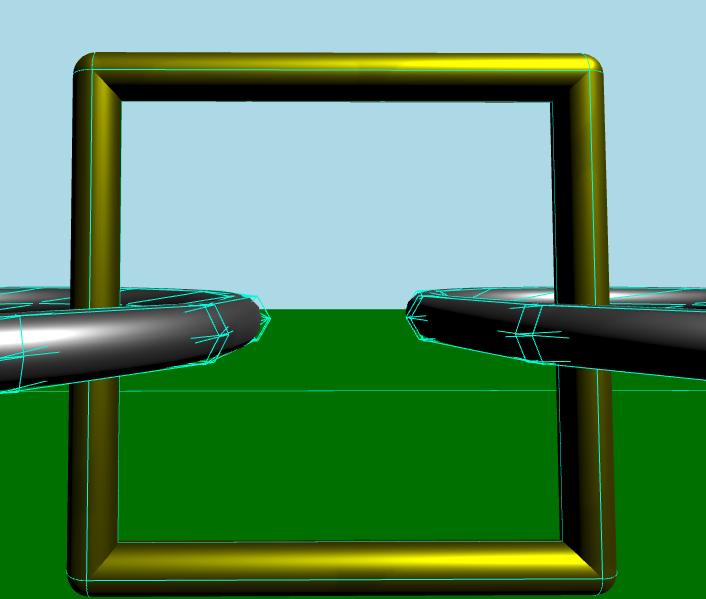
カプセルリンクは、同じ素材を共有するいくつかのモデルを持つダイナミック剛体です。このリンクは、いくつかの円柱と球から形成されています。メッシュリンクのように、コリジョンシェイプのリストがあります。今回はそれぞれのシェイプがカプセルシェイプです。
デバッグモードを有効にしてよく見ると、このようにコリジョンシェイプが複合コリジョンシェイプを形成しています。
ファイル
© 2025 The Qt Company Ltd. Documentation contributions included herein are the copyrights of their respective owners. The documentation provided herein is licensed under the terms of the GNU Free Documentation License version 1.3 as published by the Free Software Foundation. Qt and respective logos are trademarks of The Qt Company Ltd. in Finland and/or other countries worldwide. All other trademarks are property of their respective owners.

