Qt Quick 3D Physics - インペラの例
トリガーボディとコリジョン情報の使い方を説明します。
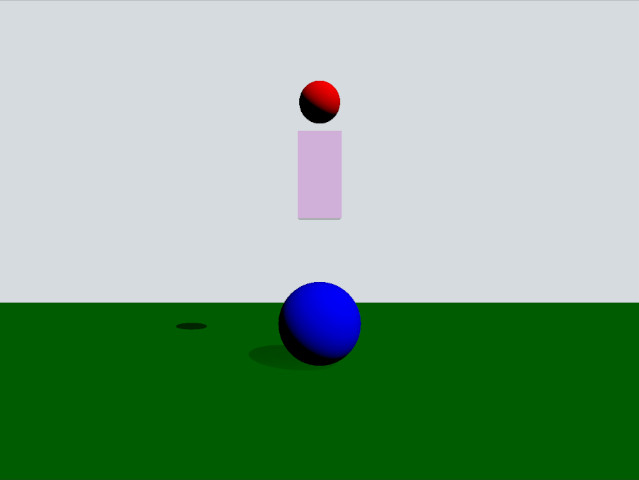
この例では、トリガーボディとコリジョン情報の使い方をデモします。シーンは、緑の静的平面、赤い動的球体、ピンクのボックストリガー、青い静的球体で構成されています。赤い球体がトリガーボディに重なると黄色に変わり、青い球体に衝突するとはじき飛ばされます。
セットアップ
いつものように、PhysicsWorld を追加する必要がある:
PhysicsWorld { gravity: Qt.vector3d(0, -490, 0) scene: viewport.scene }
また、シーンオブジェクトを置くView3D 。この中に、ビジュアル環境の設定をいくつか入れます:
environment: SceneEnvironment { clearColor: "#d6dbdf" backgroundMode: SceneEnvironment.Color } PerspectiveCamera { position: Qt.vector3d(0, 200, 1000) clipFar: 2000 clipNear: 1 } DirectionalLight { eulerRotation.x: -45 eulerRotation.y: 45 castsShadow: true brightness: 1 shadowFactor: 50 }
物理オブジェクト
通常の静的平面があります:
StaticRigidBody { position: Qt.vector3d(0, -100, 0) eulerRotation: Qt.vector3d(-90, 0, 0) collisionShapes: PlaneShape {} Model { source: "#Rectangle" scale: Qt.vector3d(500, 500, 1) materials: PrincipledMaterial { baseColor: "green" } castsShadows: false receivesShadows: true } }
これが、動的な球体を定義する方法です:
DynamicRigidBody { id: sphere massMode: DynamicRigidBody.CustomDensity density: 0.00001 position: Qt.vector3d(0, 600, 0) property bool inArea: false sendContactReports: true receiveTriggerReports: true onEnteredTriggerBody: { inArea = true } onExitedTriggerBody: { inArea = false } collisionShapes: SphereShape {} Model { source: "#Sphere" materials: PrincipledMaterial { baseColor: sphere.inArea ? "yellow" : "red" } } }
inArea というプロパティは、球体がいつボックストリガーのボディに重なったかを追跡するためのカスタムプロパティです。これはbaseColor プロパティに使用され、球体がボックスと重なっているときは黄色、重なっていないときは赤色になります。球体に接触報告をさせたいので、sendContactReports プロパティをtrue に設定する必要があります。また、TriggerBody に入るときと出るときにコールバックを取得させたいので、receiveContactReports プロパティもtrue に設定します。球体にenteredTriggerBody とexitedTriggerBody シグナルメソッドを実装し、トリガーボディに入るときと出るときに、inArea プロパティをtrue またはfalse に設定します。
次に、トリガーボディを見てみましょう:
TriggerBody { position: Qt.vector3d(0, 350, 0) scale: Qt.vector3d(1, 2, 1) collisionShapes: BoxShape { id: boxShape } Model { source: "#Cube" materials: PrincipledMaterial { baseColor: Qt.rgba(1, 0, 1, 0.2) alphaMode: PrincipledMaterial.Blend } } }
qmlタイプはTriggerBody 、衝突が不活性であることを除けば、静的ボディのように動作します。その代わりに、enteredTriggerBody とexitedTriggerBody のメソッド呼び出しが球体上でトリガーされます。
最後に、羽根車を見てみよう:
StaticRigidBody { position: Qt.vector3d(0, 0, 0) scale: Qt.vector3d(2, 2, 2) receiveContactReports: true collisionShapes: SphereShape {} Model { source: "#Sphere" materials: PrincipledMaterial { baseColor: "blue" } } onBodyContact: (body, positions, impulses, normals) => { for (var normal of normals) { let velocity = normal.times(-700) body.setLinearVelocity(velocity) } } }
これは静的ボディで、衝突コールバックを有効にするためにreceiveContactReports をtrue に設定します。コールバックbodyContact は衝突が報告されるたびに呼び出されます。このメソッドではsetLinearVelocity 、衝突の法線ベクトルの反対方向に線速度を設定し、羽根車をシミュレートします。
ファイル
© 2025 The Qt Company Ltd. Documentation contributions included herein are the copyrights of their respective owners. The documentation provided herein is licensed under the terms of the GNU Free Documentation License version 1.3 as published by the Free Software Foundation. Qt and respective logos are trademarks of The Qt Company Ltd. in Finland and/or other countries worldwide. All other trademarks are property of their respective owners.

