PySide6.QtCore.QSortFilterProxyModel¶
- class QSortFilterProxyModel¶
The
QSortFilterProxyModelclass provides support for sorting and filtering data passed between another model and a view. More…Synopsis¶
Properties¶
autoAcceptChildRowsᅟ- If true the proxy model will not filter out children of accepted rows, even if they themselves would be filtered out otherwisedynamicSortFilterᅟ- Whether the proxy model is dynamically sorted and filtered whenever the contents of the source model changefilterCaseSensitivityᅟ- The case sensitivity of the QRegularExpression pattern used to filter the contents of the source modelfilterKeyColumnᅟ- The column where the key used to filter the contents of the source model is read fromfilterRegularExpressionᅟ- The QRegularExpression used to filter the contents of the source modelfilterRoleᅟ- The item role that is used to query the source model’s data when filtering itemsisSortLocaleAwareᅟ- The local aware setting used for comparing strings when sortingrecursiveFilteringEnabledᅟ- Whether the filter to be applied recursively on children, and for any matching child, its parents will be visible as wellsortCaseSensitivityᅟ- The case sensitivity setting used for comparing strings when sortingsortRoleᅟ- The item role that is used to query the source model’s data when sorting items
Methods¶
def
__init__()def
filterRole()def
setFilterRole()def
setSortRole()def
sortColumn()def
sortOrder()def
sortRole()
Virtual methods¶
def
lessThan()
Slots¶
Signals¶
Note
This documentation may contain snippets that were automatically translated from C++ to Python. We always welcome contributions to the snippet translation. If you see an issue with the translation, you can also let us know by creating a ticket on https:/bugreports.qt.io/projects/PYSIDE
Detailed Description¶
Warning
This section contains snippets that were automatically translated from C++ to Python and may contain errors.
QSortFilterProxyModelcan be used for sorting items, filtering out items, or both. The model transforms the structure of a source model by mapping the model indexes it supplies to new indexes, corresponding to different locations, for views to use. This approach allows a given source model to be restructured as far as views are concerned without requiring any transformations on the underlying data, and without duplicating the data in memory.Let’s assume that we want to sort and filter the items provided by a custom model. The code to set up the model and the view, without sorting and filtering, would look like this:
treeView = QTreeView() //! [0] model = MyItemModel(self) treeView.setModel(model)To add sorting and filtering support to
MyItemModel, we need to create aQSortFilterProxyModel, callsetSourceModel()with theMyItemModelas argument, and install theQSortFilterProxyModelon the view:treeView = QTreeView() sourceModel = MyItemModel(self) proxyModel = QSortFilterProxyModel(self) proxyModel.setSourceModel(sourceModel) treeView.setModel(proxyModel)
At this point, neither sorting nor filtering is enabled; the original data is displayed in the view. Any changes made through the
QSortFilterProxyModelare applied to the original model.The
QSortFilterProxyModelacts as a wrapper for the original model. If you need to convert sourceQModelIndexes to sorted/filtered model indexes or vice versa, usemapToSource(),mapFromSource(),mapSelectionToSource(), andmapSelectionFromSource().Note
By default, the model dynamically re-sorts and re-filters data whenever the original model changes. This behavior can be changed by setting the
dynamicSortFilterproperty.The Basic Sort/Filter Model and Custom Sort/Filter Model examples illustrate how to use
QSortFilterProxyModelto perform basic sorting and filtering and how to subclass it to implement custom behavior.Sorting¶
QTableView and QTreeView have a sortingEnabled property that controls whether the user can sort the view by clicking the view’s horizontal header. For example:
treeView.setSortingEnabled(True)
When this feature is on (the default is off), clicking on a header section sorts the items according to that column. By clicking repeatedly, the user can alternate between ascending and descending order.
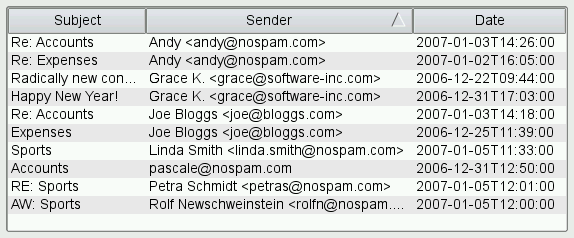
Behind the scene, the view calls the
sort()virtual function on the model to reorder the data in the model. To make your data sortable, you can either implementsort()in your model, or use aQSortFilterProxyModelto wrap your model –QSortFilterProxyModelprovides a genericsort()reimplementation that operates on thesortRole()(DisplayRoleby default) of the items and that understands several data types, includingint,QString, andQDateTime. For hierarchical models, sorting is applied recursively to all child items. String comparisons are case sensitive by default; this can be changed by setting thesortCaseSensitivityproperty.Custom sorting behavior is achieved by subclassing
QSortFilterProxyModeland reimplementinglessThan(), which is used to compare items. For example:bool MySortFilterProxyModel.lessThan(QModelIndex left, QModelIndex right) leftData = sourceModel().data(left) rightData = sourceModel().data(right) //! [4] //! [6] if leftData.userType() == QMetaType.QDateTime: return leftData.toDateTime() < rightData.toDateTime() else: emailPattern = QRegularExpression("[\\w\\.]*@[\\w\\.]*") leftString = leftData.toString() if left.column() == 1: match = emailPattern.match(leftString) if match.hasMatch(): leftString = match.captured(0) rightString = rightData.toString() if right.column() == 1: match = emailPattern.match(rightString) if match.hasMatch(): rightString = match.captured(0) return QString.localeAwareCompare(leftString, rightString) < 0(This code snippet comes from the Custom Sort/Filter Model example.)
An alternative approach to sorting is to disable sorting on the view and to impose a certain order to the user. This is done by explicitly calling
sort()with the desired column and order as arguments on theQSortFilterProxyModel(or on the original model if it implementssort()). For example:proxyModel.sort(2, Qt.AscendingOrder)
QSortFilterProxyModelcan be sorted by column -1, in which case it returns to the sort order of the underlying source model.Note
sortColumn()returns the most recently used sort column. The default value is -1, which means that this proxy model does not sort. Also, note thatsort()sets thesortColumn()to the most recently used sort column.Filtering¶
In addition to sorting,
QSortFilterProxyModelcan be used to hide items that do not match a certain filter. The filter is specified using aQRegularExpressionobject and is applied to thefilterRole()(DisplayRoleby default) of each item, for a given column. TheQRegularExpressionobject can be used to match a regular expression, a wildcard pattern, or a fixed string. For example:proxyModel.setFilterRegularExpression(QRegularExpression("\.png", QRegularExpression.CaseInsensitiveOption)) proxyModel.setFilterKeyColumn(1)
For hierarchical models, the filter is applied recursively to all children. If a parent item doesn’t match the filter, none of its children will be shown.
A common use case is to let the user specify the filter regular expression, wildcard pattern, or fixed string in a QLineEdit and to connect the textChanged() signal to
setFilterRegularExpression(),setFilterWildcard(), orsetFilterFixedString()to reapply the filter.Custom filtering behavior can be achieved by reimplementing the
filterAcceptsRow()andfilterAcceptsColumn()functions. For example (from the Custom Sort/Filter Model example), the following implementation ignores thefilterKeyColumnproperty and performs filtering on columns 0, 1, and 2:bool MySortFilterProxyModel.filterAcceptsRow(int sourceRow, QModelIndex sourceParent) index0 = sourceModel().index(sourceRow, 0, sourceParent) index1 = sourceModel().index(sourceRow, 1, sourceParent) index2 = sourceModel().index(sourceRow, 2, sourceParent) return (sourceModel().data(index0).toString().contains(filterRegularExpression()) def sourceModel().data(index1).toString().contains(filterRegularExpression())): def dateInRange(sourceModel().data(index2).toDate()):
(This code snippet comes from the Custom Sort/Filter Model example.)
If you are working with large amounts of filtering and have to invoke
beginFilterChange()/endFilterChange()repeatedly, usingbeginResetModel()/endResetModel()may be more efficient, depending on the implementation of your model. However,beginResetModel()/endResetModel()returns the proxy model to its original state, losing selection information, and will cause the proxy model to be repopulated.Subclassing¶
Since
QAbstractProxyModeland its subclasses are derived fromQAbstractItemModel, much of the same advice about subclassing normal models also applies to proxy models. In addition, it is worth noting that many of the default implementations of functions in this class are written so that they call the equivalent functions in the relevant source model. This simple proxying mechanism may need to be overridden for source models with more complex behavior; for example, if the source model provides a customhasChildren()implementation, you should also provide one in the proxy model.Note
Some general guidelines for subclassing models are available in the Model Subclassing Reference.
- class Direction¶
(inherits
enum.Flag) This enum is used to specify the direction to which a custom filter applies when the filter parameters are changed.Added in version 6.10.
Note
Properties can be used directly when
from __feature__ import true_propertyis used or via accessor functions otherwise.- property autoAcceptChildRowsᅟ: bool¶
This property holds if true the proxy model will not filter out children of accepted rows, even if they themselves would be filtered out otherwise..
The default value is false.
See also
recursiveFilteringEnabledfilterAcceptsRow()- Access functions:
- property dynamicSortFilterᅟ: bool¶
This property holds whether the proxy model is dynamically sorted and filtered whenever the contents of the source model change.
Note that you should not update the source model through the proxy model when dynamicSortFilter is true. For instance, if you set the proxy model on a QComboBox, then using functions that update the model, e.g., addItem(), will not work as expected. An alternative is to set dynamicSortFilter to false and call
sort()after adding items to the QComboBox.The default value is true.
See also
- Access functions:
- property filterCaseSensitivityᅟ: Qt.CaseSensitivity¶
This property holds the case sensitivity of the
QRegularExpressionpattern used to filter the contents of the source model..By default, the filter is case sensitive.
Note
Setting this property propagates the new case sensitivity to the
filterRegularExpressionproperty, and so breaks its binding. Likewise explicitly settingfilterRegularExpressionchanges the current case sensitivity, thereby breaking its binding.- Access functions:
- property filterKeyColumnᅟ: int¶
This property holds the column where the key used to filter the contents of the source model is read from..
The default value is 0. If the value is -1, the keys will be read from all columns.
- Access functions:
- property filterRegularExpressionᅟ: QRegularExpression¶
This property holds the
QRegularExpressionused to filter the contents of the source model.Setting this property through the
QRegularExpressionoverload overwrites the currentfilterCaseSensitivity. By default, theQRegularExpressionis an empty string matching all contents.If no
QRegularExpressionor an empty string is set, everything in the source model will be accepted.Note
Setting this property propagates the case sensitivity of the new regular expression to the
filterCaseSensitivityproperty, and so breaks its binding. Likewise explicitly settingfilterCaseSensitivitychanges the case sensitivity of the current regular expression, thereby breaking its binding.- Access functions:
- property filterRoleᅟ: int¶
This property holds the item role that is used to query the source model’s data when filtering items..
The default value is
DisplayRole.See also
- Access functions:
- property isSortLocaleAwareᅟ: bool¶
This property holds the local aware setting used for comparing strings when sorting.
By default, sorting is not local aware.
See also
- Access functions:
- property recursiveFilteringEnabledᅟ: bool¶
This property holds whether the filter to be applied recursively on children, and for any matching child, its parents will be visible as well..
The default value is false.
See also
- Access functions:
- property sortCaseSensitivityᅟ: Qt.CaseSensitivity¶
This property holds the case sensitivity setting used for comparing strings when sorting.
By default, sorting is case sensitive.
See also
- Access functions:
- property sortRoleᅟ: int¶
This property holds the item role that is used to query the source model’s data when sorting items..
The default value is
DisplayRole.See also
- Access functions:
Constructs a sorting filter model with the given
parent.- autoAcceptChildRows()¶
- Return type:
bool
See also
Getter of property
autoAcceptChildRowsᅟ.- autoAcceptChildRowsChanged(autoAcceptChildRows)¶
- Parameters:
autoAcceptChildRows – bool
This signals is emitted when the value of the
autoAcceptChildRowsproperty is changed.See also
Notification signal of property
autoAcceptChildRowsᅟ.- beginFilterChange()¶
Warning
This section contains snippets that were automatically translated from C++ to Python and may contain errors.
Prepares a change of the filter.
This function should be called if you are implementing custom filtering (e.g.
filterAcceptsRow()), and your filter parameter is about to be changed.def setFilterMaximumDate(self, date): beginFilterChange() maxDate = date endFilterChange(QSortFilterProxyModel.Direction.Rows)
Once the filter has been changed, call
endFilterChange()withRowsfor row-filters,Columnsfor column-filters, orColumns|Rowsif both rows and columns are filtered.See also
- dynamicSortFilter()¶
- Return type:
bool
See also
Getter of property
dynamicSortFilterᅟ.- dynamicSortFilterChanged(dynamicSortFilter)¶
- Parameters:
dynamicSortFilter – bool
- endFilterChange([directions=QSortFilterProxyModel.Direction.Both])¶
- Parameters:
directions – Combination of
Direction
Invalidates the current filtering after the filter parameter has changed.
This function should be called if you implement custom filtering (e.g.
filterAcceptsRow()), and your filter parameters have changed. Thedirectionsparameter specifies whether the custom filter impacts rows, columns, or both.Call
beginFilterChange()when the filter parameter is about to change, and follow with a call to this function once the filter parameters have been changed. Call withdirectionsset toRowsfor row-filters (i.e.filterAcceptsRow()is implemented),Columnsfor column-filters (i.e.filterAcceptsColumn()is implemented), orDirection::Bothif both filter functions are implemented.- filterAcceptsColumn(source_column, source_parent)¶
- Parameters:
source_column – int
source_parent –
QModelIndex
- Return type:
bool
Returns
trueif the item in the column indicated by the givensource_columnandsource_parentshould be included in the model; otherwise returnsfalse.Note
The default implementation always returns
true. You must reimplement this method to get the described behavior.- filterAcceptsRow(source_row, source_parent)¶
- Parameters:
source_row – int
source_parent –
QModelIndex
- Return type:
bool
Returns
trueif the item in the row indicated by the givensource_rowandsource_parentshould be included in the model; otherwise returns false.The default implementation returns
trueif the value held by the relevant item matches the filter string, wildcard string or regular expression.Note
By default, the
DisplayRoleis used to determine if the row should be accepted or not. This can be changed by setting thefilterRoleproperty.- filterCaseSensitivity()¶
- Return type:
See also
Getter of property
filterCaseSensitivityᅟ.- filterCaseSensitivityChanged(filterCaseSensitivity)¶
- Parameters:
filterCaseSensitivity –
CaseSensitivity
This signal is emitted when the case sensitivity of the filter changes to
filterCaseSensitivity.Notification signal of property
filterCaseSensitivityᅟ.- filterKeyColumn()¶
- Return type:
int
See also
Getter of property
filterKeyColumnᅟ.- filterRegularExpression()¶
- Return type:
See also
Getter of property
filterRegularExpressionᅟ.- filterRole()¶
- Return type:
int
See also
Getter of property
filterRoleᅟ.- filterRoleChanged(filterRole)¶
- Parameters:
filterRole – int
This signal is emitted when the filter role changes to
filterRole.Notification signal of property
filterRoleᅟ.- invalidate()¶
Invalidates the current sorting and filtering.
See also
- invalidateColumnsFilter()¶
Note
This function is deprecated.
use
beginFilterChange()andendFilterChange(Rows) instead.Invalidates the current filtering for the columns.
This function should be called if you are implementing custom filtering (by
filterAcceptsColumn()), and your filter parameters have changed. This differs frominvalidateFilter()in that it will not invokefilterAcceptsRow(), but onlyfilterAcceptsColumn(). You can use this instead ofinvalidateFilter()if you want to hide or show a column where the rows don’t change.Before your filter parameters change, call
beginFilterChange().- invalidateFilter()¶
Note
This function is deprecated.
Warning
This section contains snippets that were automatically translated from C++ to Python and may contain errors.
use
beginFilterChange()andendFilterChange()instead.Invalidates the current filtering.
This function should be called if you are implementing custom filtering (e.g.
filterAcceptsRow()), and your filter parameters have changed.Before your filter parameters change, call
beginFilterChange().def setFilterMaximumDate(self, date): beginFilterChange() maxDate = date endFilterChange(QSortFilterProxyModel.Direction.Rows)
- invalidateRowsFilter()¶
Note
This function is deprecated.
use
beginFilterChange()andendFilterChange(Columns) instead.Invalidates the current filtering for the rows.
This function should be called if you are implementing custom filtering (by
filterAcceptsRow()), and your filter parameters have changed. This differs frominvalidateFilter()in that it will not invokefilterAcceptsColumn(), but onlyfilterAcceptsRow(). You can use this instead ofinvalidateFilter()if you want to hide or show a row where the columns don’t change.Before your filter parameters change, call
beginFilterChange().- isRecursiveFilteringEnabled()¶
- Return type:
bool
Getter of property
recursiveFilteringEnabledᅟ.- isSortLocaleAware()¶
- Return type:
bool
Getter of property
isSortLocaleAwareᅟ.- lessThan(source_left, source_right)¶
- Parameters:
source_left –
QModelIndexsource_right –
QModelIndex
- Return type:
bool
Returns
trueif the value of the item referred to by the given indexsource_leftis less than the value of the item referred to by the given indexsource_right, otherwise returnsfalse.This function is used as the < operator when sorting, and handles the following
QVarianttypes:Any other type will be converted to a
QStringusingtoString().Comparison of
QStrings is case sensitive by default; this can be changed using thesortCaseSensitivityproperty.By default, the
DisplayRoleassociated with theQModelIndexes is used for comparisons. This can be changed by setting thesortRoleproperty.Note
The indices passed in correspond to the source model.
See also
- recursiveFilteringEnabledChanged(recursiveFilteringEnabled)¶
- Parameters:
recursiveFilteringEnabled – bool
This signal is emitted when the recursive filter setting is changed to
recursiveFilteringEnabled.Notification signal of property
recursiveFilteringEnabledᅟ.- setAutoAcceptChildRows(accept)¶
- Parameters:
accept – bool
See also
Setter of property
autoAcceptChildRowsᅟ.- setDynamicSortFilter(enable)¶
- Parameters:
enable – bool
See also
Setter of property
dynamicSortFilterᅟ.- setFilterCaseSensitivity(cs)¶
- Parameters:
cs –
CaseSensitivity
See also
Setter of property
filterCaseSensitivityᅟ.- setFilterFixedString(pattern)¶
- Parameters:
pattern – str
Sets the fixed string used to filter the contents of the source model to the given
pattern.This method will reset the regular expression options but respect case sensitivity.
Note
Calling this method updates the regular expression, thereby breaking the binding for
filterRegularExpression. However it has no effect on thefilterCaseSensitivitybindings.- setFilterKeyColumn(column)¶
- Parameters:
column – int
See also
Setter of property
filterKeyColumnᅟ.- setFilterRegularExpression(regularExpression)¶
- Parameters:
regularExpression –
QRegularExpression
See also
Setter of property
filterRegularExpressionᅟ.- setFilterRegularExpression(pattern)
- Parameters:
pattern – str
Sets the regular expression used to filter the contents of the source model to
pattern.This method should be preferred for new code as it will use
QRegularExpressioninternally.This method will reset the regular expression options but respect case sensitivity.
Note
Calling this method updates the regular expression, thereby breaking the binding for
filterRegularExpression. However it has no effect on thefilterCaseSensitivitybindings.- setFilterRole(role)¶
- Parameters:
role – int
See also
Setter of property
filterRoleᅟ.- setFilterWildcard(pattern)¶
- Parameters:
pattern – str
Sets the wildcard expression used to filter the contents of the source model to the given
pattern.This method will reset the regular expression options but respect case sensitivity.
Note
Calling this method updates the regular expression, thereby breaking the binding for
filterRegularExpression. However it has no effect on thefilterCaseSensitivitybindings.- setRecursiveFilteringEnabled(recursive)¶
- Parameters:
recursive – bool
See also
Setter of property
recursiveFilteringEnabledᅟ.- setSortCaseSensitivity(cs)¶
- Parameters:
cs –
CaseSensitivity
See also
Setter of property
sortCaseSensitivityᅟ.- setSortLocaleAware(on)¶
- Parameters:
on – bool
See also
Setter of property
isSortLocaleAwareᅟ.- setSortRole(role)¶
- Parameters:
role – int
See also
Setter of property
sortRoleᅟ.- sortCaseSensitivity()¶
- Return type:
See also
Getter of property
sortCaseSensitivityᅟ.- sortCaseSensitivityChanged(sortCaseSensitivity)¶
- Parameters:
sortCaseSensitivity –
CaseSensitivity
This signal is emitted when the case sensitivity for sorting changes to
sortCaseSensitivity.Notification signal of property
sortCaseSensitivityᅟ.- sortColumn()¶
- Return type:
int
Returns the column currently used for sorting
This returns the most recently used sort column. The default value is -1, which means that this proxy model does not sort.
See also
sort()- sortLocaleAwareChanged(sortLocaleAware)¶
- Parameters:
sortLocaleAware – bool
This signal is emitted when the locale aware setting changes to
sortLocaleAware.Notification signal of property
isSortLocaleAwareᅟ.Returns the order currently used for sorting
This returns the most recently used sort order. The default value is
AscendingOrder.See also
sort()- sortRole()¶
- Return type:
int
See also
Getter of property
sortRoleᅟ.- sortRoleChanged(sortRole)¶
- Parameters:
sortRole – int
This signal is emitted when the sort role changes to
sortRole.Notification signal of property
sortRoleᅟ.